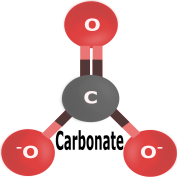
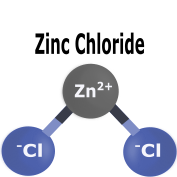
 |
Chlorides and chloride salts tend to be highly soluble in water and will generally dissolve in other common solvents as well. |
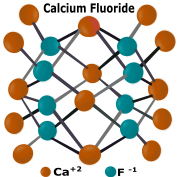 |
Fluorides and their salts are most commonly employed in the industrial process of hydrofloric acid. Many fluorides and are also well-known to the glass making industry and contribute to many of the particular qualities of specialty glass and their products; particularly optical glass. Soluble fluorides may react with water and form hydrofluoric acid. Alkaline earth metal-fluoride ion salts such as magnesium fluoride, tend to be mostly insoluble. |
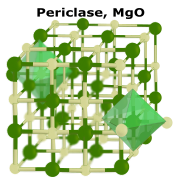 |
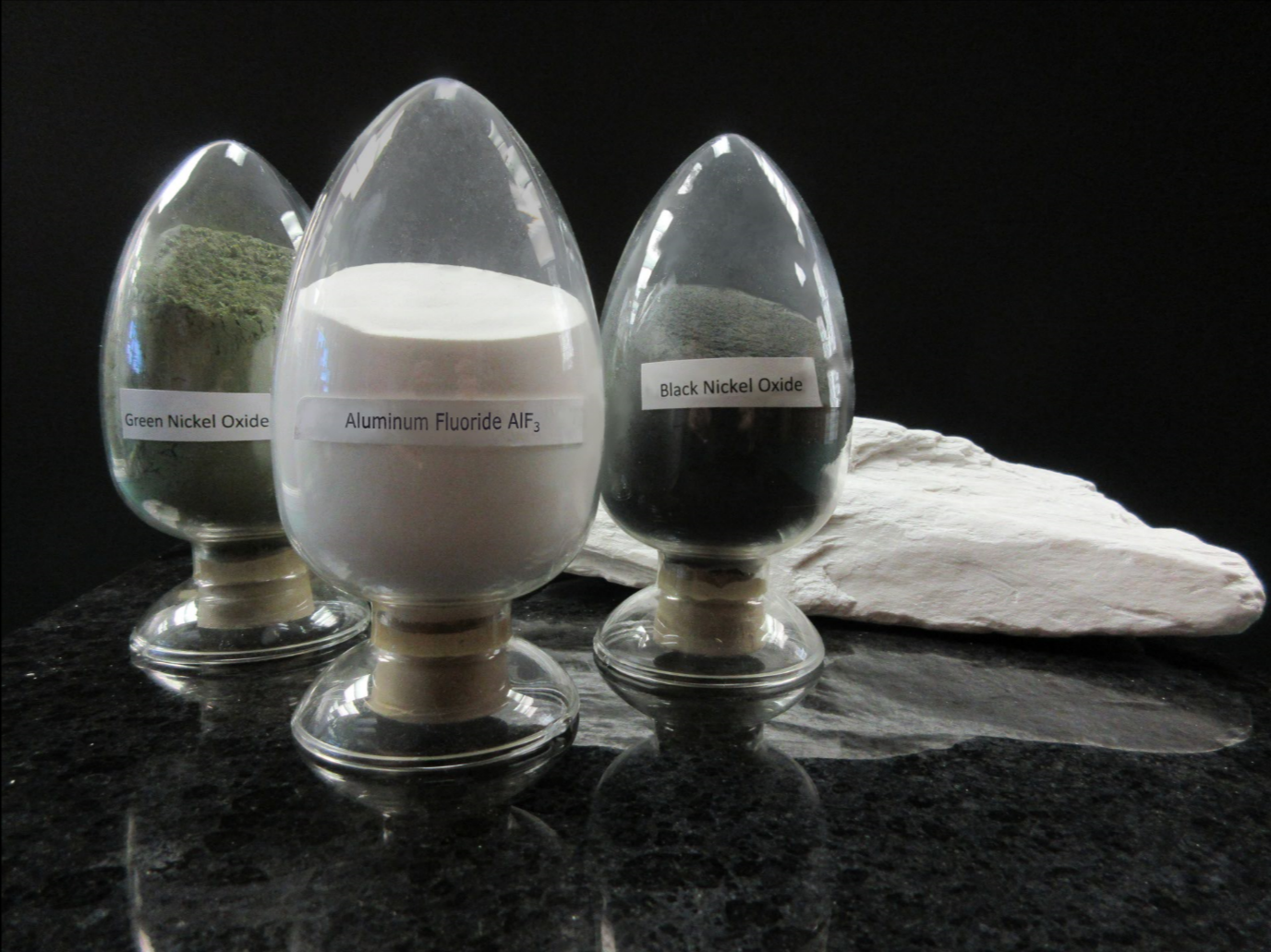
Metal Oxides consist of a metal element and oxygen. They are typically basic and considered weak bases, water insoluble, and form salts in reaction to acid (acid-base reaction). Chemical structure for metal oxides often look like a box with pipes inside of it. |
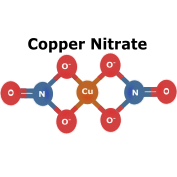 |
Nitrate Salts are inorganic salts that tend to be soluble in both water and ammonium. Alkaline earth nitrates if thermally decomposed, release nitrogen dioxide. Although these salts are most renown for their usage in fertilizers and explosives, they have many other uses as well. For instance, sodium nitrate is used to cure meats and calcium nitrate is used in waste water treatment and cement production. |
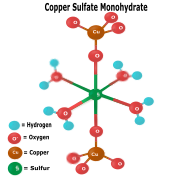 |
Sulfates typically have several or more water molecules to their O oxygen ones. Examples include magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (aka:Epsom salt), copper sulfate heptahydrate, and-. |
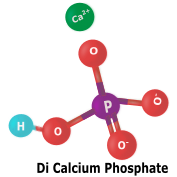 |
Phosphates are inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. They are used to create phosphates for animal feed nutrients, fertilizer, and other phosphate chemicals. Calcium phosphate is an important nutrient for milk, bones, teeth, and many other biofuntions. |